Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakatsuka, Toru; Tamai, Hidesada; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The subchannel analysis code NASCA was applied to critical power prediction of 37-rod tight-lattice bundle experiments which JAERI has been carrying out to confirm the thermal-hydraulic feasibility of the RMWR. The NASCA can yield good predictions of critical power for the gap width of 1.3 mm while the prediction accuracy of critical power deteriorated in case of the gap width of 1.0 mm. Predicted BT positions agree with the experimental results. Models in the code will be improved to consider the effect of the gap width based on further studies in the future.
Liu, W.; Onuki, Akira; Tamai, Hidesada; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2005/10
In this research, the newest version of critical power correlation for tight-lattice rod bundles is proposed by using 7-rod and 37-rod bundle data derived in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). For comparatively high mass velocity region, the correlation is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. For low mass velocity region, it is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. The correlation is verified by JAERI data and Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data. It is confirmed the correlation is able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The correlation is further implemented into TRAC code to analyze flow decrease and power increase transients. It is confirmed transient BT can be predicted within the accuracy of the implemented critical power correlation.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Nakatsuka, Toru; Misawa, Takeharu; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
R&D project to investigate thermal-hydraulic performance in tight-lattice rod bundles for Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) is started at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute in collaboration with power company, reactor vendors, universities since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured LWR technologies. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight-lattice configuration. In this paper, we will show the R&D plan and describe some advances on experimental and analytical studies. Steady-state and transient critical power experiments have been conducted with two 37-rod bundle test facilities (Gap width between rods: 1.3mm and 1.0mm) and the experimental data reveal the feasibility of RMWR.
Kobayashi, Noboru; Okubo, Tsutomu; Uchikawa, Sadao
JAERI-Review 2005-029, 119 Pages, 2005/09
The research on Innovative Water Reactor for Flexible fuel cycle (FLWR) has been performed in JAERI for the development of future innovative reactors. The workshop on the FLWRs has been held every year since 1998 aiming at information exchange between JAERI and other organizations. The 8th workshop was held on Feb. 10, 2005 under the joint auspices of JAERI and North Kanto and Kanto-Koetsu branches of Atomic Energy Society of Japan with 75 participants. The workshop began with 3 presentations on FLWRs entitled "Framework and Status of Research and Development on FLWRs", "Long-Term Fuel Cycle Scenarios for Advanced Utilization of Plutonium from LWRs", and "Experiments on Characteristics on Hydrodynamics in Tight-Lattice Core". Then 3 lectures followed: "Development of Evaluation Method for Accuracy in Predicting Neutronics Characteristics of Tight-Lattice Core" by Osaka University, "Development of Cost-Reduced Low-Moderation Spectrum Boiling Water Reactor" by Toshiba Corporation and "Design and Analysis on Super-Critical Water Cooled Power Reactors" by Tokyo University.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Nakatsuka, Toru; Akimoto, Hajime
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2005-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu, Vol.3, p.207 - 208, 2005/09
We started R&D project to develop the predictable technology for thermal-hydraulic performance of Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) in collaboration with power company/reactor vendor/university since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured BWR technologies. MOX fuel assemblies with tight lattice arrangement are used to increase the conversion ratio by reducing the moderation of neutron energy. Increasing the in-core void fraction also contributes to the reduction of neutron moderation. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight lattice configuration and the high void fraction. This presentation shows the advances of thermal/hydraulic feasibility study using large-scale test facility and advanced numerical simulation technology.
Akimoto, Hajime; Tamai, Hidesada; Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki
Nihon Konsoryu Gakkai Nenkai Koenkai 2005 Koen Rombunshu, p.229 - 230, 2005/08
A thermal-hydraulic research program for Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) has been performed since 2002. The RMWR has a tight-lattice core to attain the breeding of nuclear fuel for the effective use of Plutonium in a light-water reactor system. In this R&D program, large-scale thermal-hydraulic tests, several model experiments and development of advanced numerical analysis codes are being carried out to confirm the cooling performance in tight-lattice fuel assembly of the RMWR. In this paper, outline of the research program is described as well as the latest results of critical power measurement in the large-scale thermal-hydraulic tests and model experiments, which simulates the tight-lattice core of the RMWR.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Nakatsuka, Toru; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-13) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/05
R&D project to investigate thermal-hydraulic performance in tight-lattice rod bundles for Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) is started at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute in collaboration with power company, reactor vendors, universities since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured LWR technologies. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight-lattice configuration. In this paper, we will show the R&D plan and describe some advances on experimental and analytical studies. The experimental study is performed mainly using large-scale (37-rod bundle) test facility and the analytical one aims to develop a predictable technology for geometry effects such as gap between rods etc. using advanced 3-D two-phase flow simulation methods. Steady-state and transient critical power experiments are conducted with the test facility (Gap width between rods: 1.3mm and 1.0mm) and the experimental data reveal the feasibility of RMWR.
Liu, W.; Tamai, Hidesada; Onuki, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Sato, Takashi; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of 2005 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '05) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2005/05
A major concern in the design of RMWR is that sufficient cooling capability be provided to keep fuel cladding temperature below specified values, even for a postulated abnormal transient process. In this research, centered the postulated transient cases that may be possibly met in the RMWR running, transient BT tests are performed in 7-rod and 37-rod double-humped tight lattice bundles, under the RMWR nominal operating condition (P = 7.2 MPa, Tin =556 K) for mass velocity G = 300 - 800 kg / (m s). Experiments are analyzed with TRAC code, in which JAERI critical power correlation is implemented for BT judgment. The traditional quasi-steady-state prediction of BT in transient process is confirmed being applicable for the postulated nominal transients in the RMWR cores.
s). Experiments are analyzed with TRAC code, in which JAERI critical power correlation is implemented for BT judgment. The traditional quasi-steady-state prediction of BT in transient process is confirmed being applicable for the postulated nominal transients in the RMWR cores.
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi; Onuki, Akira; Akimoto, Hajime
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 42(1), p.40 - 49, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this research, critical power correlation for tight-lattice rod bundles is newly proposed using 7-rod axially uniform-heated data, 7-rod and 37-rod axially double-humped-heated data at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). For low mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region (
s), the correlation is written in critical quality - annular flow length type. For high mass velocity region ( 300 kg/m
300 kg/m s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m
s), it is written in local critical heat flux - critical quality type. The standard deviation of ECPR (Experimental Critical Power Ratio) to the whole JAERI data (694 data points) is 6%. The correlation is verified by Bettis Atomic Power Laboratory data (177 points, standard deviation: 7.7%). The correlation is confirmed being able to give good prediction for the effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure and heated equivalent diameter on critical power. The applicable range of the correlation is: gap between rods from 1.0 to 2.29 mm, heated length from 1.26 to 1.8 m, mass velocity from 150 to 2000 kg/m s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
s and pressure from 2 to 11 MPa.
Mitsutake, Toru*; Akimoto, Hajime; Misawa, Takeharu; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Katsuyama, Kozo*; Nagamine, Tsuyoshi*; Matsumoto, Shinichiro*
Proceedings of 4th World Congress on Industrial Process Tomography, Vol.1, p.348 - 353, 2005/00
An inside-structure observation of a tight-lattice 7-rod bundle was made, using the high-energy X-ray computer tomography(CT) apparatus. The two-dimensional configurations of all rods were obtained at seventy-six axial height positions over the whole length of the bundle. The measured results of the rod positions showed small rod position displacements, about 0.5 millimeters at maximum, from the lattice positions. Based on these measured rod position displacement results, the flow area, equivalent hydraulic diameter, rod-rod clearance, and rod-shroud clearance were calculated. The effect of rod position displacement on critical power was estimated by a sub-channel analysis. The result showed that the rod position displacement effect has only a small effect on critical power calculations. The calculated critical power still overestimated the measured value.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of Japan-US Seminar on Two-Phase Flow Dynamics, p.317 - 325, 2004/12
We start R&D project to develop the predictable technology for thermal-hydraulic performance of Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) in collaboration with Power Company/reactor vendor/university since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured BWR technologies. MOX fuel assemblies with tight lattice arrangement are used to increase the conversion ratio by reducing the moderation of neutron energy. Increasing the in-core void fraction also contributes to the reduction of neutron moderation. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight lattice configuration. In this paper, we will show the R&D plan and describe the current status on experimental and analytical studies. We will confirm the thermal-hydraulic performance in the tight-lattice bundles by this project and develop a predictable technology for the RMWR in future.
Takase, Kazuyuki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Ose, Yasuo*; Tamai, Hidesada
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics, Operations and Safety (NUTHOS-6) (CD-ROM), 14 Pages, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Nagayoshi, Takuji*; Ose, Yasuo*; Takase, Kazuyuki; Akimoto, Hajime
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 3(3), p.233 - 241, 2004/09
When there are no experimental data such as the reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR), therefore, it is very difficult to obtain highly precise predictions. The RMWR core adopts a hexagonal tight lattice arrangement with about 1 mm gap between adjacent fuel rods. In the core, there is no sufficient information about the effects of the gap spacing and grid spacer configuration on the flow characteristics. Thus, we start to develop a predictable technology for thermal-hydraulic performance of RMWR core using advanced numerical simulation technology. As part of this technology development, we are developing advanced interface tracking method to improve conservation of volume of fluid. In this paper, we describe a newly developed interface tracking method and examples of the numerical results. In the present results, the error of volume conservation in the bubbly flow is within 0.6%.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Akie, Hiroshi; Kugo, Teruhiko; Yonomoto, Taisuke; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Nagaya, Yasunobu; Araya, Fumimasa; Okajima, Shigeaki; et al.
JAERI-Research 2004-008, 383 Pages, 2004/06
The present report contains the achievement of "Research and Development on Reduced-Moderation Light Water Reactor with Passive Safety Features", which was performed by Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI), Hitachi Ltd., Japan Atomic Power Company and Tokyo Institute of Technology in FY2000-2002 as the innovative and viable nuclear energy technology (IVNET) development project operated by the Institute of Applied Energy (IAE). In the present project, the reduced-moderation water reactor (RMWR) has been developed to ensure sustainable energy supply and to solve the recent problems of nuclear power and nuclear fuel cycle, such as economical competitiveness, effective use of plutonium and reduction of spent fuel storage. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as high burnup, long operation cycle, multiple recycling of plutonium (Pu) and effective utilization of uranium resources based on accumulated LWR technologies.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Akimoto, Hajime
Proceedings of 2004 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP '04), p.1488 - 1494, 2004/06
We start R&D project to develop the predictable technology for thermal-hydraulic performance of Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) in collaboration with power company/reactor vendor/university since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources based on matured BWR technologies. MOX fuel assemblies with tight lattice arrangement are used to increase the conversion ratio by reducing the moderation of neutron energy. Increasing the in-core void fraction also contributes to the reduction of neutron moderation. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR. This series presentation focuses on the feasibility study and shows the R&D plan using large-scale test facility and advanced numerical simulation technology.
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi; Akimoto, Hajime
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(2), p.299 - 305, 2004/05
Experimental research on critical power in tight lattice bundle that simulates the Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) has been carried out in Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI). The bundle consists one center rod and six peripheral rods. The 7 rods are arranged on a 14.3 mm equilateral triangular pitch. Each rod is 13 mm in outside diameter. An axial 12-step power distribution is employed to simulate the complicate heating condition in RMWR. Experiments are carried out under  = 100-1400 kg/m
= 100-1400 kg/m s,
s, 
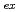 = 2-8.5 MPa. Effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure, radial peaking factor and axial peaking factor on critical power and critical quality are discussed. Compared with axial uniform heating condition, the axial non-uniform heating condition causes an obvious decrease in critical quality. Arai correlation, which is the only correlation that has been optimized for tight lattice condition, is verified with the present experimental data. The correlation is found to be able to give reasonable prediction only around RMWR nominal operating condition.
= 2-8.5 MPa. Effects of mass velocity, inlet temperature, pressure, radial peaking factor and axial peaking factor on critical power and critical quality are discussed. Compared with axial uniform heating condition, the axial non-uniform heating condition causes an obvious decrease in critical quality. Arai correlation, which is the only correlation that has been optimized for tight lattice condition, is verified with the present experimental data. The correlation is found to be able to give reasonable prediction only around RMWR nominal operating condition.
Okubo, Tsutomu
Konsoryu, 17(3), p.228 - 235, 2003/09
The Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor is supposed to realize plutonium multiple recycling, and furthermore, plutonium breeding cycle, based on the well-established Light Water Reactor technologies. In the present paper, the overview of the design study is presented and the related R&D issues are introduced, especially focusing on the thermal hydraulic activities.
Nakatsuka, Toru; Tamai, Hidesada; Kureta, Masatoshi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Akimoto, Hajime; Iwamura, Takamichi
Proceedings of International Conference on Global Environment and Advanced Nuclear Power Plants (GENES4/ANP 2003) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2003/09
It is important to evaluate thermal margin of the tight lattice core in the Reduced-Moderation Water reactor (RMWR). In the present study, to assess the applicability of subchannel analysis for tight lattice cores, tight lattice CHF experiments were analyzed with COBRA-TF code. For the axial uniform heated rod bundle, the code gives good prediction of critical power for mass velocity of around 500kg/(m s), while the code underestimates it for lower mass velocity and overestimates for higher mass velocity. The predicted BT position was outer channels and differed from the measured position. For the axially double-humped heated bundle, the code gives good prediction for mass velocity of around 200kg/(m
s), while the code underestimates it for lower mass velocity and overestimates for higher mass velocity. The predicted BT position was outer channels and differed from the measured position. For the axially double-humped heated bundle, the code gives good prediction for mass velocity of around 200kg/(m s), and overestimates for higher mass velocity. It turned out that the two-phase multiplier of friction loss have a large influences on the flow distribution among the subchannels. To improve the calculation accuracy, it is required to predict precisely the flow distribution including the prediction of pressure distribution in a tight lattice bundle.
s), and overestimates for higher mass velocity. It turned out that the two-phase multiplier of friction loss have a large influences on the flow distribution among the subchannels. To improve the calculation accuracy, it is required to predict precisely the flow distribution including the prediction of pressure distribution in a tight lattice bundle.
Onuki, Akira; Takase, Kazuyuki; Kureta, Masatoshi; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Tamai, Hidesada; Liu, W.; Akimoto, Hajime
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2003-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu, Vol.3, p.247 - 248, 2003/08
We start R&D project to develop the predictable technology for thermal-hydraulic performance of Reduced-Moderation Water Reactor (RMWR) in collaboration with power company/reactor vendor/university since 2002. The RMWR can attain the favorable characteristics such as effective utilization of uranium resources, multiple recycling of plutonium, high burn-up and long operation cycle, based on matured BWR technologies. MOX fuel assemblies with tight lattice arrangement are used to increase the conversion ratio by reducing the moderation of neutron energy. Increasing the in-core void fraction also contributes to the reduction of neutron moderation. The confirmation of thermal-hydraulic feasibility is one of the most important R&D items for the RMWR because of the tight lattice configuration. This series presentation focuses on the feasibility study and shows the R&D plan using large-scale test facility and advanced numerical simulation technology.
Onuki, Akira; Shibata, Mitsuhiko; Tamai, Hidesada; Akimoto, Hajime; Yamauchi, Toyoaki*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nihon Konsoryu Gakkai Nenkai Koenkai 2003 Koen Rombunshu, p.35 - 36, 2003/07
Analytical evaluation of maximum critical power by so-called subchannnel code is indispensable for design of reduced moderation water reactor. In this study, two-phase flow distribution in a tight-lattice rod bundle is investigated using 19-rod bundle experimental rig and subchannnel analysis code NASCA. The flow distribution was measured under so-called churn flow regime and the predictive capability of NASCA was assessed. NASCA can predict the flow distribution qualitatively depending on local pressure drop. Quantitative prediction is also reasonable for liquid phase but the gas phase distribution was underestimated. Void-drift model has a dominant contribution and we should improve the model for the tight-lattice rod bundle.